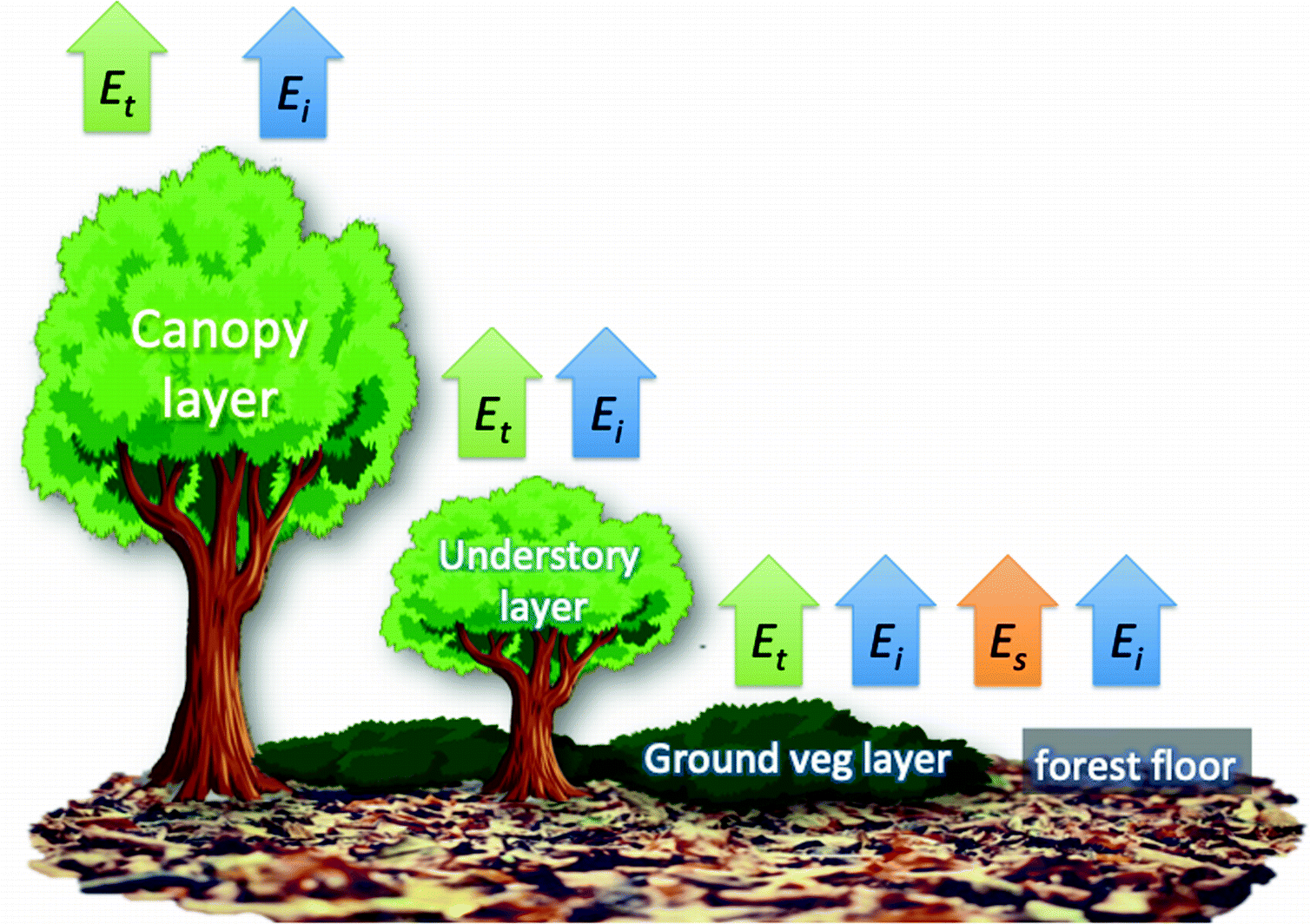
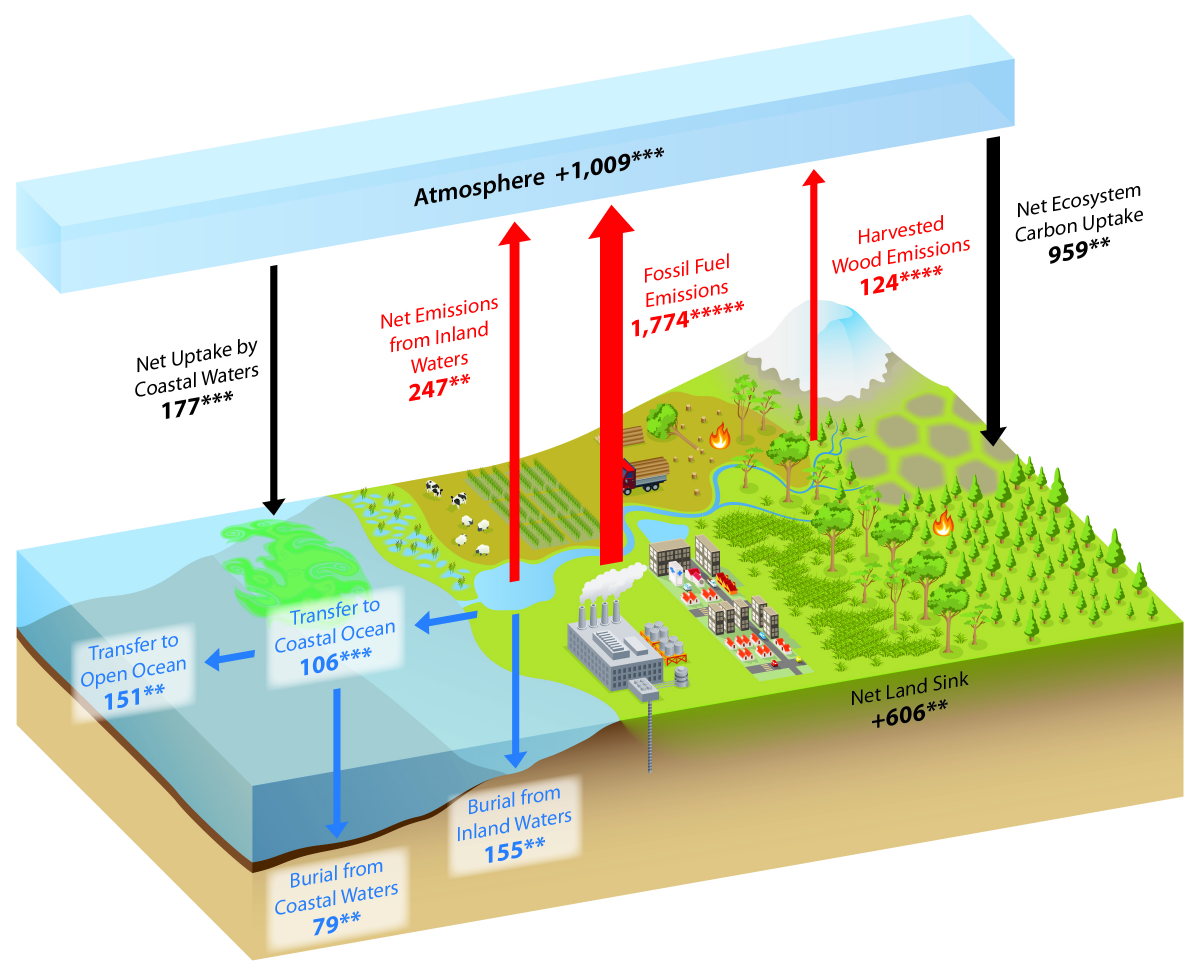
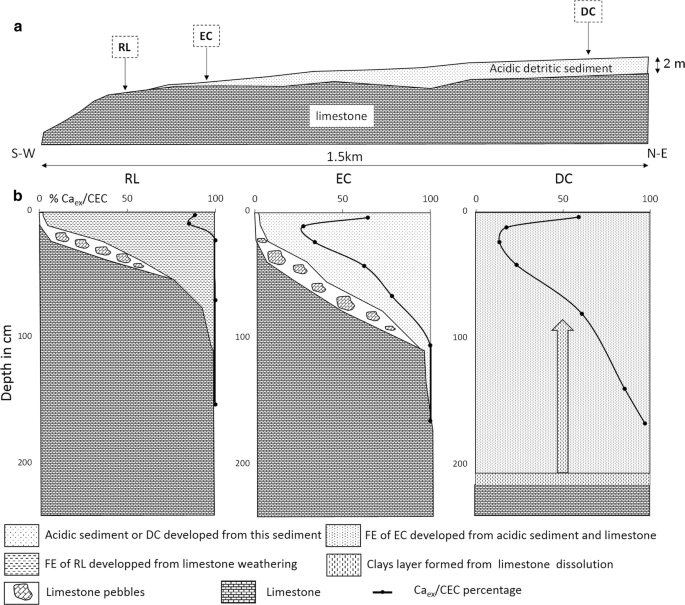
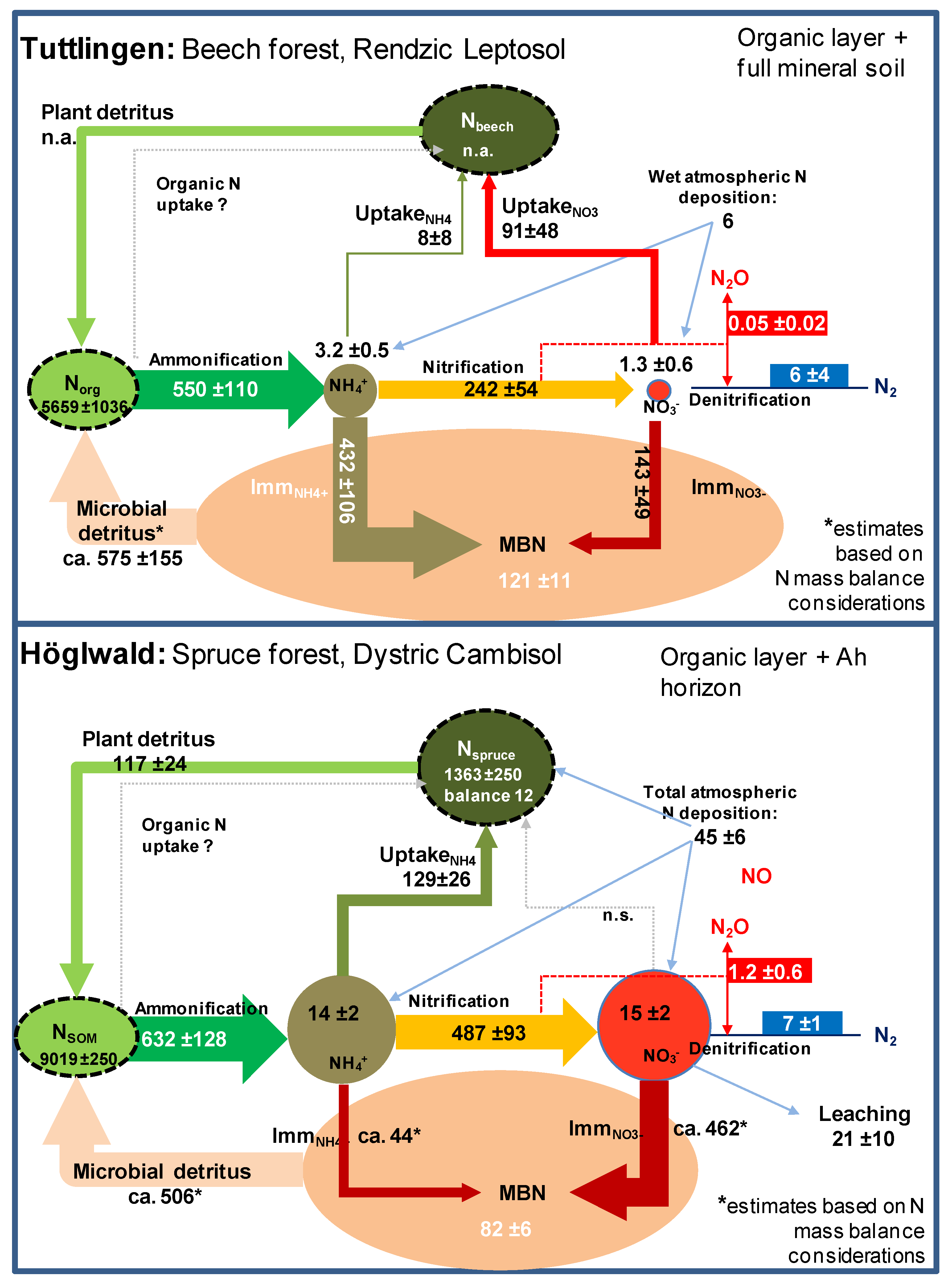
The Residence Time Of Litter On The Forest Floor Increases

1 two stands within this age class that were treated with nonlethal understorey fires in 1962 and 1963 stand nos.
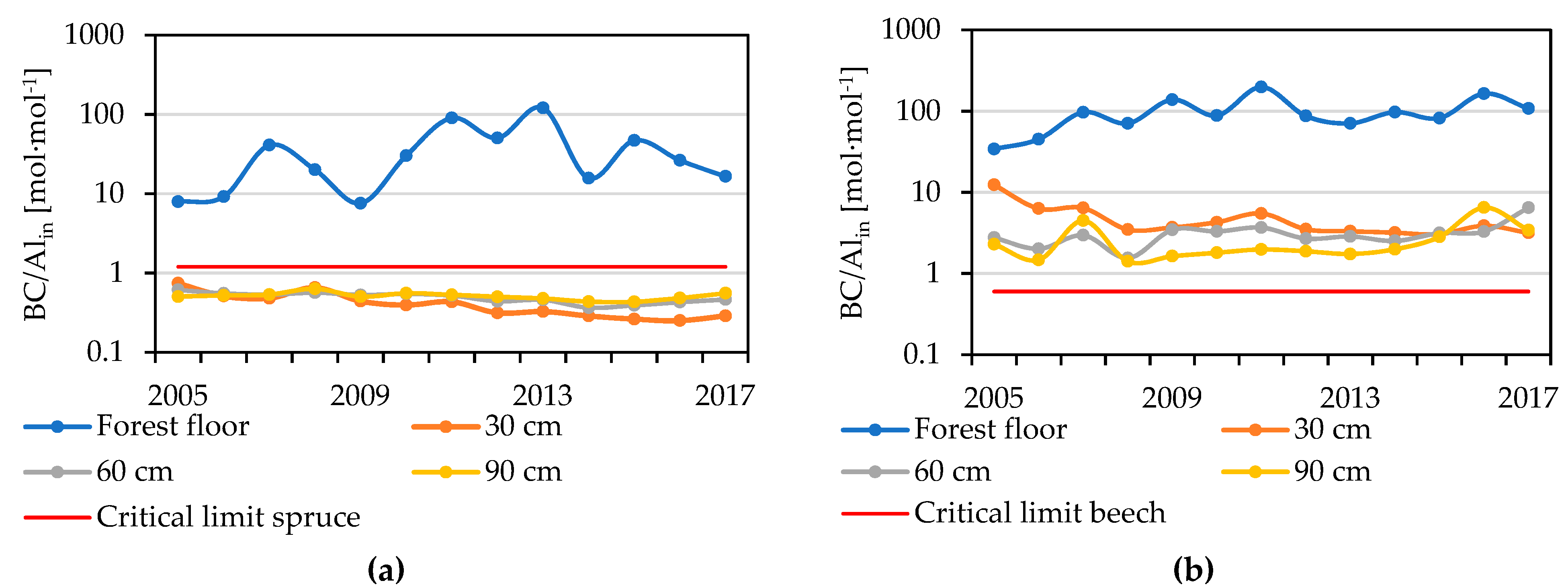
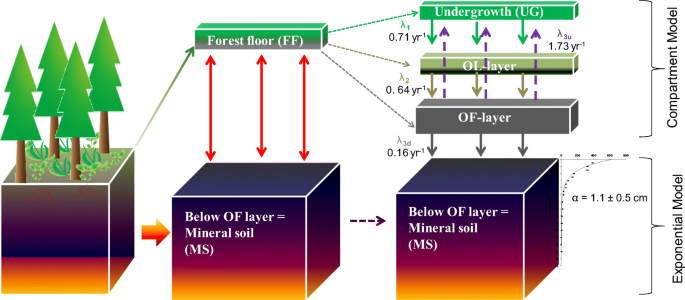
The residence time of litter on the forest floor increases. The residence time in each compartment t r i increased with depth from 1 10 0 35 years for compartment l to 2 59 1 86 years for compartment f2b. A time period where the megaphona were dying off from human interactions and increase in population about 10 000 years ago. The mean residence time of litter is calculated as 1 k slow. Leaf litter decomposition rates were a positive linear function of mat causing the residence time of leaf litter on the forest floor to decline by 31 days for each 1 c increase in mat.
The size of the compartments was similar. Decomposition litter fall and nutrient and organic matter turnover rates were determined in five eastern ontario jack pine pinusbanksiana lamb stands having various burning histories including wildfire the stands included a 65 year old age class stand no. 2 and 3. Leaf tissue can account for more than 70 of above ground litter fall in forests and the rest is composed of stems small twigs and propagative structures robertson and paul 1999.
Our estimate of the q 10 temperature coefficient for leaf litter decomposition was 2 17 within the commonly reported range for heterotrophic organic matter decomposition 1 5 2 5 across a broad range of ecosystems. Leaf litter decomposition rates were a positive linear function of mat causing the residence time of leaf litter on the forest floor to decline by 31 days for each 1 c increase in mat. Our estimate of the q10 temperature coefficient for leaf litter decomposition was 2 17 within the commonly reported range for heterotrophic organic matter decomposition 1 5 2 5 across a broad range of ecosystems. Leaf litter decomposition rates were a positive linear function of mat causing the residence time of leaf litter on the forest floor to decline by 31 days for each 1 c increase in mat.
Prediction of soil macroporosity based on litter input. The mean residence time of the forest floor is the standing stock divided by the annual litter inputs. Leaf litter decomposition rates were a positive linear function of mat causing the residence time of leaf litter on the forest floor to decline by 31 days for each 1 c increase in mat. Our estimate of the q 10 temperature coefficient for leaf litter decomposition was 2 17 within the commonly reported range for heterotrophic organic matter decomposition 1 5 2 5 across a broad range of ecosystems.
The science art business and practice of conserving and manufacturing forests and land to provide a sustained supply of forest products forest conditions and forest value. Litter fall in terrestrial ecosystems signifies a crucial pathway for nutrient return to the soil. The forest floor is a major reservoir of organic matter and nutrients for the ecosystem and as such it influences or regulates most of the functional processes occurring throughout the ecosystem. Litter mass loss or decay is the sum of carbon dioxide co 2 release and discharge of compounds.