The Lowering Of The Desert Floor As Wind Eroded Sediments
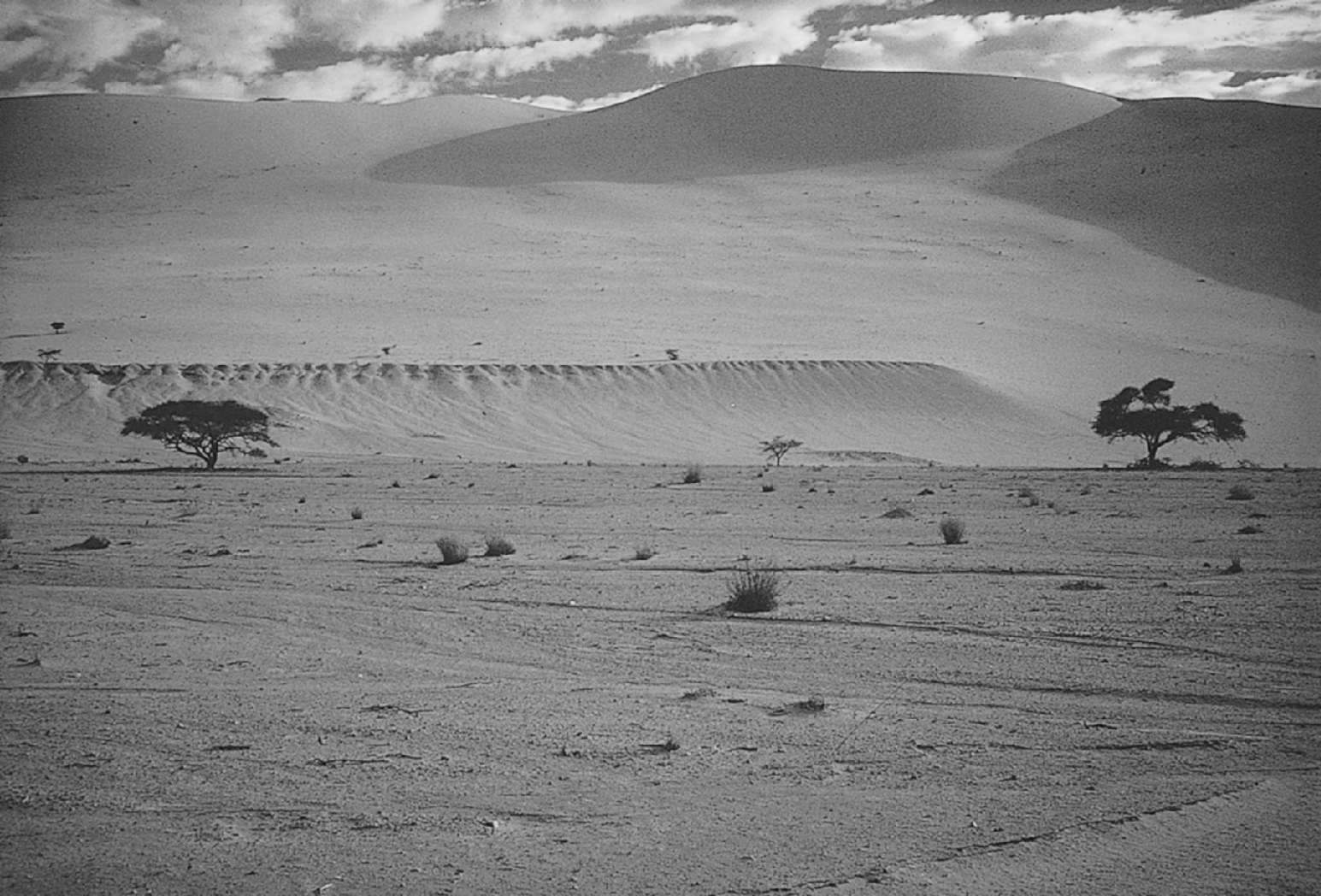
Winds in the desert are often extreme and unrestricted by trees and vegetation.
The lowering of the desert floor as wind eroded sediments. The lowering of the desert floor when wind removes the smallest sand particles abrasion the wearing away of an object caused by the direct contact between moving particles. Water is also able to erode land by the effects of currents and ocean waves. Now a german geologist has analyzed lakebed sediments to shed. As a grain strikes another grain or surface it erodes that surface.
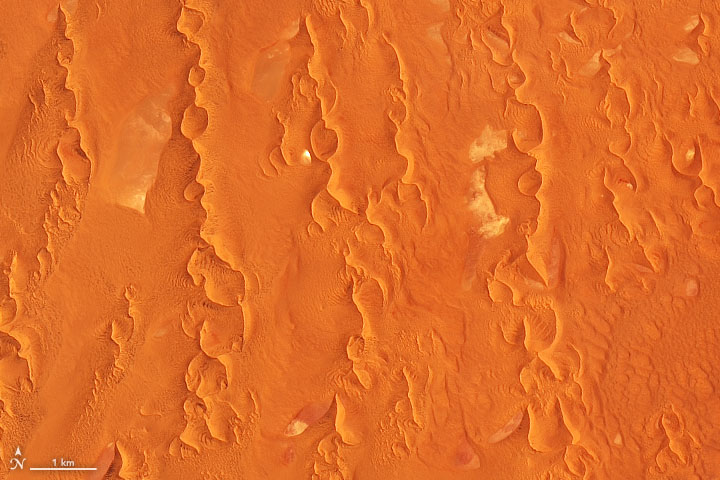
Sand dunes are common wind deposits that come in different shapes depending on winds and sand availability. Deflation is the lowering of the land surface due to removal of fine grained particles by the wind. Wind can carry small particles such as sand silt and clay. When the wind blows across loose sediment it removes small particles like clay silt and sand leaving the courser heavier sediment behind.
This process of removing lighter sediment is called deflation. Loess is a very fine grained wind borne deposit that can be important to soil formation. Deflation concentrates the coarser grained particles at the surface eventually resulting in a surface composed only of the coarser grained fragments that cannot be transported by the wind. The ground actually gets lower over time and those heavier sediments become quite firm in the ground.
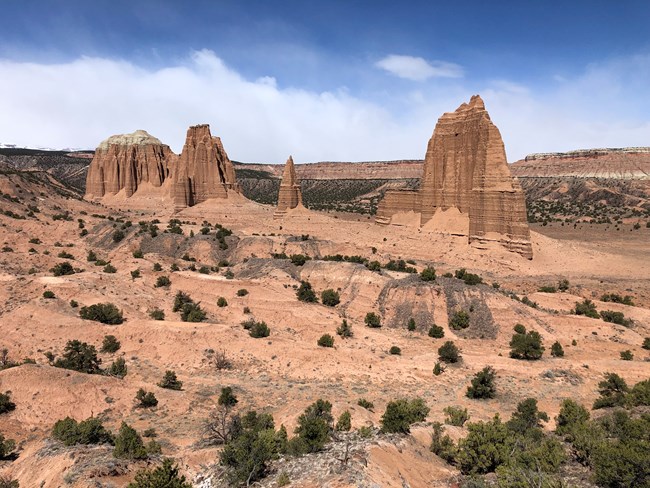
Typically made out of sedimentary rocks usually sandstone laid down in horizontal layers this layering generally makes the zeugen flat topped and stepped in profile because most abrasion is concentrated within a metre or so of the desert floor zeugen often have a slightly narrower more eroded lower portion. In arid regions small particles are selectively picked up and transported. Wind can be an effective erosion and transportation agent if it is strong and blows across fine grained sediment such as sand silt and clay. Once the eroded particles as a result of ocean currents and waves are settled and deposited they enormously change the coastline of the area.
A fan shaped deposit of sediment formed when a stream s slope is abruptly reduced alluvial fan a flat area on the floor of an undrained desert basin playa that fills and becomes heavy rain. A wind s bed load consists of the heavier grains usually sand that hop and skip along the ground by saltation. Wind erosion abrades surfaces and makes desert pavement ventifacts and desert varnish. As they are removed the ground surface gets lower and rockier causing deflation.